Role of Merchandising
 Role and Responsibilities of Merchandiser in Apparel Industry
Role and Responsibilities of Merchandiser in Apparel IndustryWhat is Merchandising?
Merchandising denotes all the planned activities to executive
and dispatched the merchandise on time taking into consideration the
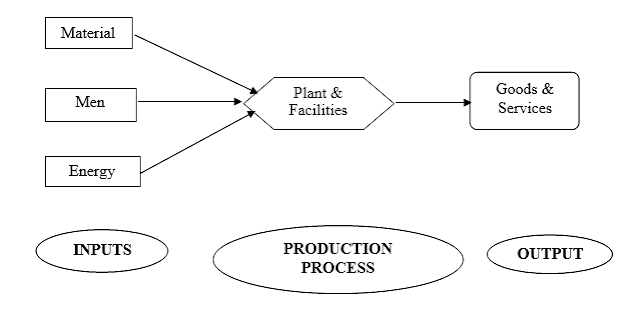
4 R’s of expending right cost, right quantity, right quality and right time to replenish the customers.
Functions Involved In Merchandising
1. Execution of sample orders
2. Costing
3. Programming
4. yarn procurement arrangements
5. Production scheduling (or) Route card
drafting
6. Accessories arrangement (order
placing follow-ups)
7. Approval of various processors sewing
operations and finishing processes
8. Pattern approval (or) dummy size set
approval
9. Size set approval
10. Pre-production sample follow-ups
11. Pilot run inspection
12. In-processes inspection
13. Production controlling
14. Identifying shortages and make
arrangement for the shortages
15. Shortage quantity and quality
following quality control procedures
16. Following quality assurance
procedures
17. Maintaining the juniors activities of
in-house and subcontractor units
18. Buyers communication
19. Communication with production units,
processing units and other third party’s (vendors)
20. Proper reporting
21. Highlighting the management
22. Record maintenance (records
pertaining to merchandising)
23. Developing samples
24. Placement of orders
25. Taking measures for consistent
production
26. Taking preventive actions to maintain
the targeted performance level in all areas of merchandising
27. Attending meeting with superiors and
furnishing the required details about merchandising
How the Sample Order Executed?
After the receipt of the
specification, pertaining to the sample order, the merchandiser has to
understand what are the requirements of buyers sometimes there may be
amendments related to any of the specifications in the sample order sheet. It
is the duty of the merchandiser to execute sample order and dispatch on time
the “right quality”.
Costing Making
In many companies costing is done by
costing officer and CEO. In some companies it is done by the merchandisers
should know the following details.
1. Yarn quality
2. Process cost (knitting, bleaching,
rising etc.
3. Rates pertaining to various sewing
operations
4. CMT rates
5. Ironing, packing charges +
accessories rate
6. Overheads
7. Shortage (or) wastage 3 %
8. Free on Board (7.0.B) ( Transport
charges) 2 % of 3 %
9. Insurance 2 % - 3 %
10. Buyer agents commission 5% - 6% quota rate per garment
11. Profit 15 % - 20 %
Technical Programming Process
Most probably programming is done by
CEO (or) productions manager. In some companies it is done the merchandisers.
The following factors should be considered in programming
1. Allowances
a. Fabric Structure
b. Dia fixation (knitting dia,
calendaring dia and compacting dia)
c. Process loss (shrinkage etc.)
d. Size wise piece weight
e. Extra quantity required
f. Size wise requirement (dia, color or
combination)
Route card drafting (or) production
For each and the every order route
card (or) production scheduling is to be the merchandisers. It facilitates the
merchandiser to follow up the orders. In a planned manner. The following
details (or) aspects should be considered in drafting (or) scheduling.
1. Design
2. No. of sewing operations
3. No. of processes
4. dispatch date
5. No. of components
6. Type of stitches
7. order Quantity
8. Production capacity of the in-houses
(or) subcontractors unit and processing units
9. Prioritizing
The other factors
10. Targeted dates for various processes
(or) stages of merchandising
11. actual finishing date (to cross check
the deviation between the planning and actual performance of any stage (or)
process)
targeted dates for all the stages of
merchandising should be decided. Actual dates which a particular process (or)
operation is actually done should also be entered in production scheduling. The
merchandisers an accountable for the deviation.
Accessories arrangement Plans
Merchandiser has to make arrangements for the timely
delivery of the required accessories to the concerned units. Accessories
requisition slip may be used for requirement purpose. The merchandiser has to
cross check the actual requirements after verifying the details furnished in
accessories requisition form. After the receipt of accessories quality check
can be done.
Pattern Approvals
Patterns should be approved for
1. Measurement
2. Style and fit
3. Allowances
4. Accuracy of pattern
If there is any non-conformance in
patterns that should be corrected before it is used in production. Pattern
approval samples will be received from the concerned units and approved by the
approval department (or) merchandisers. If there is non-conformance in any size
submitted for approval.
Size set approvals
Size set approvals are made by the
approval department (or) by the merchandisers. All the quality parameters
related to various processes, sewing operations have be cross checked the below
mentioned aspects should be considered.
1. Measurements
2. Asethetics
3. Process Qulaity
4. ASM
5. Piece shrinkage
6. Washing fastness of the piece
7. Sewing operation quality (SPI and
stitch width)
8. print (or) embroidery position
9. Labeling instructions
Size
set approval seat will be prepared in triplicate.
10. Washing fastness of garment should be
verified
11. Shrinkage in garment can also be
verified
Pre-production Sample Making
This samples should be submitted on
time to the concerned person (buyer, buyer agents office, buying office). All
the quality parameters have to be verified. In case of non-conformance it will
be mentioned in the approval seat by the concerned persons. Sometime, we may
have to submit the revised samples after the required rectifications.
Pilot run Inspection With Buyer
Pilot run denotes the first
production garments quality parameters are verified and preventive measures can
be taken. The follow-up team should do pilot run inspection to identify the
various defects and it will be verified in production.
In-process Inspection
In-process means in between any
process (or) sewing operation (or) any activities related to executive of an
order. We can have procedures for frequency and adequacy. In case of major
non-conformities we have to highlight the problems of quality at the right time
to the right person without fail/ consistent follow-up inspection is a must to
confirm that all the quality procedures are adopted by the concerned units and
preventive actions are taken to enhance the performance.
Production Controlling
Controlling should be right form the
operatives level also. Efforts should be taken to control the non-conformities
during production. Consistent supervision is essential to control the non
conformance. Periodical quality check should be done after an hour.
Shortage Problem
The merchandiser has to identify the
shortages of any material that is yarn, fabric, accessories etc. right at the
initial stages. After identifying the shortages steps are to be taken for the
arrangement of required materials on time. In case of shortages also we have to
follow the quality control and quality assurance, procedure without fail.
Quality of the material should not be compromised.
Following Quality control Procedures
Some companies written quality
procedures are available in quality manual. The merchandiser has to know all
the procedures of quality control. In all procedures should be followed very
strictly. It has to inculcate the importance of procedures to subordinates,
in-house units (or) own units, and subcontractors.
Following quality assurance procedures
All the required test procedures (as
required by the buyer) should be followed very strictly without partiality.
Evidences for testing (test reports tested samples tested swatches tested
accessories) should be maintained properly. Before cutting the merchandiser has
to confirm that the concerned unit has got all the required approvals properly
form the authorized person.
Monitoring the juniors activities
The merchandiser has to monitor his
sub-ordinates. He has to teach to the subordinates about the quality
procedures. He have to give instructions to them. Before going for factory
visit he has to discuss the various activities to be executed on a particular
day. The merchandiser has to control the activities of the subordinates so that
the performance of the followed team is good.
Monitoring the activities of
subordinators (or) In-house units
The merchandiser has to monitor the
activities of in-house units (or) sub-contractor units. He has to confirm that
all the quality control procedures and quality assurance procedures are
follow-up properties of adopting quality procedures to attending the planned
performance level.
Buyer communication
The merchandiser has to go through
the faxes coming from buyer and he has to send reply on time, sometimes he has
to furnish the production status of a particular orders to the concerned buyer
on time. The below mentioned are some of the duties of buyer communication.
1. Sample execution
2. Amendments
3. Comments on the send samples
4. Sample order sheet
5. Buyer visit
6. Production status
7. sending sample swatches accessories
regarding the approvals
Communication with others
The merchandiser has to interact with
in-house units, sub-contractors, vendors and job workers of various processing.
Through proper interaction only we make arrangement for the timely supply of
the required materials to the concerned persons. He has to know the production
status from various units which will be helpful in proper follow and proper
importing.
Proper importing
The merchandiser has to furnish (or)
bestow the report to the right person at the right time. He has to give reports
for the below mentioned activities:
1.
Sample
execution
2.
Approvals
3.
Testing
procedures
4.
Production
status
5.
Programming
6.
Shortage
details
7.
Inspection
details and status
8.
Production
status for meeting etc.
9.
Report from inspection agencies, testing labs
(SITRA, TEXAN LAB, S. G> S INUQUE
Inspection Centres)
Highlighting
The merchandiser has to highlight the major problems in
merchandising at the right time without fail. Highlighting will facilitate the
supervisor’s to take the necessary steps to tackle the problems on time. Proper
decision is made due to timely highlighting.
Record maintenance
The merchandiser has to maintain
quality records pertaining to various buyer orders. Proper filing should be
done, who can utilize the services of subordinates in record maintenance. The
below mentioned are some examples.
1. Sample details
Sample inspection reports
2. Testing reports
3. Evidence of approvals
4. Proper filing (buyer wise, order
wise)
(P. O. Sheet &
amendment sheet)
5. Pattern approval sheet / size set
approval sheet (copy)
6. Pilot run inspections – report
7. Fabric inspection report
8. Mid inspection report
9. Inspection report from buying office,
buying agents and inspection agencies
10. Test reports from inspection agencies
and labs
11. Production status reports
12. Production status reports related to meetings
13. Pre-final inspection reports
14. Final inspection reports etc.
Developing Samples
Some buyers will give specifications
(or) diagrams (or) patterns from which you may have to develop samples. Samples
may be fabric with required knit structure (or) garment with required with specification.
The merchandiser has to consider all the quality parameters related t the
samples to be developed in case of non-conformities in the samples developed.
Revised samples may be send for approval purpose. It is the duty of the
merchandiser to dispatch the developed samples on time to the concerned buyers
by means of a consistent follow-up.
Placement of orders
Priority is given to “Approval sub-contractors after evaluation (
when the production capacity is not sufficient) order is placed to new manufacturer
also. Orders can be placed to in-house units also. In some companies,
merchandiser is accountable (or) responsible to find out the right
manufacturer’s after proper evaluation. All the initial stages small quantity
orders will be placed. After verifying their performance large quantity orders
will be placed. Yarn may be produced by the concerned unit (or) it may be
supply by the supplier (the main manufacturer). In case of CMT orders after the
confirmation of average piece weight of a particular size, processed fabric is
delivered to the concerned unit by the supplier.
Taking measures for consistent production
It is the duty of the merchandiser to
monitor the merchandising activities in accordance with the production
scheduling. He is accountable for the execution of each and every process (or)
an operation with the targeted time. He has to take the necessary step for the
consistent production by taking the problems in merchandising.
1. quality of yarn
2. replacing good quality yarn
3. consistent arrangement for the timely
supply of accessories
4. shortage quantities follow-up
Preventive actions
detection of defects is not only the
duty of merchandiser. He has to take preventive actions to eliminate deviations
in all the stages of merchandising.
Attending meetings with superiors
Meetings may be conducted for general
discussions about order execution (or) for implementing new systems like ISO
(or) it may be a status meeting. In case of production status meeting the
production status details about various buyers
order will be collected by the merchandiser is accountable to answer the
various questions raised by the superiors pertaining to the execution of the
allotted orders.
Merchandising terminology
(1) Supplier
The manufacturer (or)
exporter who enters into a contract with a buyer. He has to 4R’s right cost,
right quality, right quantity and right time. In execution of an export order
(2) Sub-contractor
A person (manufacturer)
who executes an export order on behalf of the supplier. The export order may be
placed as merchant order (or) CMT order
(3) Direct Order
It is an export directly
taken from a buyer on some agreed specifications and conditions
(4) Merchant export
A merchant exporter will
take an export order from the main supplier (or) from buying office (or) buying
agencies. The experience in merchant order execution is a must to enter into a
direct order
(5) Evaluation of subcontractors
Sub-contractors
(6)
Vendors do supply the
required materials such as yarn, sewing threads, other accessories to
manufacturers. They will be evaluated after considering some factors, that is terms and conditions of delivery,
timely delivery, quality of the material supplied etc. after proper evaluation
a list of approved sub-contractors will be prepared. The priority goes to these
approved sub-contractors in placements of orders
(7) Vendors in evaluation
(8) Vendors do supply the required
materials such as yarn, sewing threads, other accessories to manufacturers.
They will be evaluated after considering some factors, that is terms and
conditions of delivery timely delivery, quality of the materials
supplied etc. non value

Comments
Post a Comment